Underwater data centers are an innovative and sustainable solution for the growing demand of cloud services. In this blog post, I will share with you some of the benefits and challenges of this emerging technology, and how it can transform the future of data storage and processing.
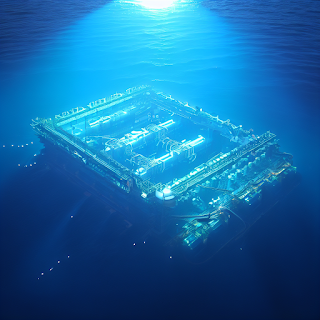 |
| Project Natick |
What are underwater data centers?
- Underwater data centers are submerged facilities equipped with power and cooling infrastructure that house computer servers. They are designed to be deployed quickly and easily in coastal areas, where most of the world's population and internet users live. Underwater data centers can deliver capacity without using valuable land, can be energy efficient thanks to the cool water of the sea, and can be positioned close to human populations, which are largely centered on the world's coasts.
- Have you ever wondered what it would be like to have a data center under the sea? Well, Microsoft has been working on an amazing project that aims to do just that! Project Natick is an experimental data center undergoing research and development by Microsoft. It seeks to understand the benefits and difficulties in deploying subsea datacenters worldwide.
- Why subsea datacenters, you may ask? There are several advantages to this innovative idea. First of all, subsea datacenters can reduce latency by being closer to the users who need them. For example, more than half of the world's population lives within 120 miles of the coast. By placing datacenters near coastal cities, Microsoft can provide faster and more reliable cloud services to millions of people. Second, subsea datacenters can leverage renewable energy sources such as wind, wave, and tidal power. This can reduce the environmental impact and operational costs of running datacenters. Third, subsea datacenters can benefit from the natural cooling effect of the ocean water. This can improve the efficiency and performance of the servers and reduce the need for air conditioning.
Microsoft deployed its first undersea data center prototype in August 2015. It was a small-scale test that lasted for 105 days and proved that the concept was feasible. It has subsequently deployed and retrieved a "shipping-container" sized data center off the coast of the Northern Isles in Scotland. This was a larger-scale experiment that lasted for two years and demonstrated that the subsea datacenter was reliable and durable. Microsoft subcontracted Naval Group, a leader in marine engineering, to spearhead the design and manufacture of the vessel. The project aims to research the feasibility of subsea datacenters powered by offshore renewable energy.
The project has been successful so far, with Microsoft having deployed a full-scale datacenter module in the North Sea, powered by renewable energy from a nearby wind farm. The module contains 864 servers and 27.6 petabytes of storage. It is connected to the internet by a fiber-optic cable and monitored remotely by Microsoft engineers. The module is expected to operate for up to five years without maintenance.
Project Natick is a visionary project that showcases Microsoft's commitment to innovation and sustainability. It is also a fascinating example of how technology can adapt to different environments and challenges. By exploring the potential of subsea datacenters, Microsoft is paving the way for a more connected and greener future.
Why are they beneficial?
One of the main benefits of underwater data centers is their power efficiency, especially in regions where the grid on land is not considered reliable enough to operate them sustainably. By placing data centers underwater, they can leverage the natural cooling of the ocean and reduce the need for artificial cooling for the servers, which is one of the major sources of energy consumption in conventional data centers. Moreover, underwater data centers can also harness renewable energy from the movement of seawater or from offshore wind farms, making them more environmentally friendly.
Another benefit of underwater data centers is their rapid provisioning. They can be built and deployed in a matter of months, compared to years for land-based data centers. This allows them to respond quickly to the changing needs and demands of customers and markets. Underwater data centers can also be easily scaled up or down by adding or removing server capsules as needed.
